SYMPTOMS
Breathing Difficulties in Dogs - Understanding Dyspnea and Tachypnea
페이지 정보
본문


What are breathing difficulties in dogs?
Breathing problems in dogs can occur due to a variety of problems with the respiratory system or other organs in their body. The respiratory system includes the nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, airway, lungs, and bronchi. A normal respiratory rate for a resting dog ranges from 10 to 30 breaths per minute, and breathing should not seem labored (forced). Monitoring and knowing how your dog breathes normally at rest, on walks, and after heavy exercise can make it easier to recognize when your dog is experiencing breathing problems as soon as possible. Respiratory problems can occur in all breeds and ages and can be life-threatening. Therefore, it is essential to understand the different types of breathing difficulties your dog may experience and seek veterinary attention promptly if you notice any signs.
Causes of breathing problems in dogs
Breathing problems in dogs can be divided into dyspnea, tachypnea, and abnormal panting.
Dyspnea (labored breathing)
Labored breathing, or forced breathing, refers to breathing with difficulty that is characterized by an increased effort to breathe. Dyspnea can be divided into two cases where it is difficult to inhale (inspiratory dyspnea) and cases where it is difficult to exhale (expiratory dyspnea).
Causes of dyspnea include:
-
Nose
Small nostrils, infections, tumors, foreign bodies, etc.
-
Larynx:
Soft palate elongation, tumor, foreign body, etc.
-
Airway:
Tracheal collapse
-
Lungs
Infections such as pneumonia, pulmonary edema due to heart failure, heart enlargement, heartworm disease, tumors, pulmonary hemorrhage, trauma, etc.
-
Bronchial tubes
Infections, tumors, allergies, inflammatory problems such as asthma, chronic bronchitis, etc.
-
Chest cavity
Pleural space due to heart failure from the accumulation of air, blood, or other fluids in the chest cavity, or tumor, infection, trauma, etc.
-
Chest wall
Trauma or partial paralysis by mites
-
Diaphragm
Trauma, congenital hernia, muscle problems, etc.
-
Intra-abdominal infections that put pressure on the diaphragm
IAI can cause an enlargement of the liver, stomach, and spleen, air in the stomach, fluid in the abdominal cavity, tumors, etc.
Tachypnea (rapid breathing)
Tachypnea refers to breathing quickly and common causes include:
-
Hypoxemia
When the concentration of oxygen in the blood is low
-
Anemia
Insufficient number of red blood cells in the blood
-
Blood clots in pulmonary vessels
-
Pulmonary edema, pulmonary hemorrhage, etc.
-
Causes of dyspnea can also cause tachypnea
Abnormal breathing or panting
-
High body temperature:
Can be considered normal panting when hot or after exercise
-
Pain
-
Anxiety
-
Hyperthyroidism
-
Causes of dyspnea and tachypnea can also cause abnormal panting
Symptoms that accompany the different types of breathing problems in dogs
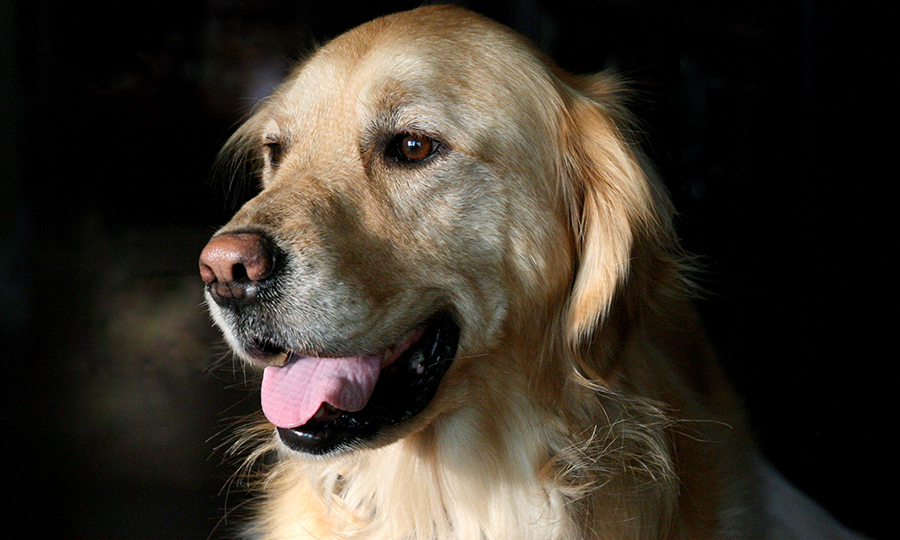

Symptoms that can accompany dyspnea
- Chest or stomach moves more than usual while breathing
- Nostrils are wide open while breathing
- Open mouth breathing
- Elbows stick outwards and breathe
- Breathing with neck and face down
- Strange sounds accompany breathing
Symptoms that can accompany tachypnea
- Respiration rate is shallower and faster than usual
- Mouth is closed or only partially open
Abnormal breathing symptoms
- Shallow and faster breathing rate, mouth wide open, tongue sticking out
- If panting persists when no hot weather or exercise was experienced
Other symptoms to look out for when your dog is having breathing difficulties
- Exercise intolerance
- A persistent cough (especially late at night)
- Any signs of anxiety, restlessness, or pacing
- Cyanosis, characterized by a pale or bluish mucous membrane
Risk of breathing difficulties in dogs
The following types and breeds of dogs may be more prone to breathing difficulties than other breeds.
-
Brachycephalic breeds
Have a higher risk of nostril stenosis, soft palate elongation, and pulmonary tumors which can cause breathing difficulties.
-
Giant breed dogs
Have a higher risk of cardiomyopathy and heart failure which can cause breathing difficulties.
-
Small or toy-breed dogs
Have a higher risk of tracheal collapse and chronic bronchitis which can cause breathing difficulties.
-
Obesity can cause breathing problems as well
How to manage breathing problems in dogs at home
Breathing problems can indicate an emergency and it is recommended to consult a veterinarian as soon as possible. If there are concerns about your pet’s breathing at home, you can check their respiratory rate first. The typical respiratory rate for dogs is between 10 and 30 breaths per minute. Ensure that your dog is resting comfortably when checking their respiratory rate. You want to count how many times their stomach rises and falls, that is considered as 1 breath, in 15 seconds. Multiply that number by 4 to get your respiratory rate and compare it to the typical respiratory rate of a healthy dog. In the meantime, ensure that your dog stays out of overly hot, humid, or dry environments until you have found the exact cause of the breathing difficulties.
To relieve symptoms even further, oxygen therapy can be administered at home. Avoid using any irritants such as perfumes, cigarette smoke, dust, etc. that can aggravate their respiratory system. Limit their exercise and activity until their breathing problems are under control. If the difficulties persist, it is vital to seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Diagnosing breathing difficulties in dogs

Your veterinarian may ask you the following questions when visiting a hospital for breathing difficulties:
- When and how did your dog’s breathing problems begin?
- Under what conditions do the breathing problems occur?
- How is your pet’s overall health?
- Has there been anything unusual recently, like trauma or excessive exercise?
Based on your answers, the following tests can be performed for a more accurate diagnosis. If breathing difficulties are severe, the dog is first stabilized with oxygen and then tested.
-
Physical examination
A veterinarian will observe the dog's breathing. Using an instrument like the stethoscope to listen to the sound of their heart and lungs, check the color of the mucous membranes, and assess their coughing by touching the airways.
-
Blood, urine, and stool test
Infections, anemia, and abnormalities in systemic organs can be identified through these tests.
-
Chest X-ray
The structure of the heart, lungs, and thoracic cavity can be checked.
-
Heart and abdominal ultrasound
Abnormalities of the heart and abdominal organs can be identified.
-
Rhinoscopy and bronchoscopy
The endoscope allows direct examination of the nose and trachea.
Treatment for breathing difficulties in dogs
If breathing difficulties are severe, stabilization with oxygen is required. Treatment will be tailored to the underlying cause of the shortness of breath identified by the examination.
Depending on the cause, treatment may include:
- Steroids may be prescribed for bronchial inflammation.
- Bronchodilators may be prescribed if the trachea/bronchi are narrowed.
- Diuretics may be prescribed if your dog has pulmonary edema.
How to prevent breathing difficulties in dogs
It's easier to spot breathing problems if you know how your dog breathes normally when resting and after walks and playtime. This way you can spot a difference as soon as possible and address it with your veterinarian when an abnormality in their breathing is heard. To avoid respiratory irritation, it is recommended to avoid perfume, cigarette smoke, and dust when around your pet. Proper weight management is also important because obese pets are more susceptible to respiratory diseases.
Find out more about your dog’s symptoms and diseases on the Buddydoc app!
The Buddydoc library is filled with everything you’d want to know about each symptom and disease your pet may experience. If you would like to find out more about the causes, signs, treatments, preventions, and more for your dog’s disease. Try out the Buddydoc app and search for your pet’s symptoms or diseases in the Buddydoc library.