SYMPTOMS
Circling in Dogs - Common Causes and Concerns for Circling Behavior
페이지 정보
본문
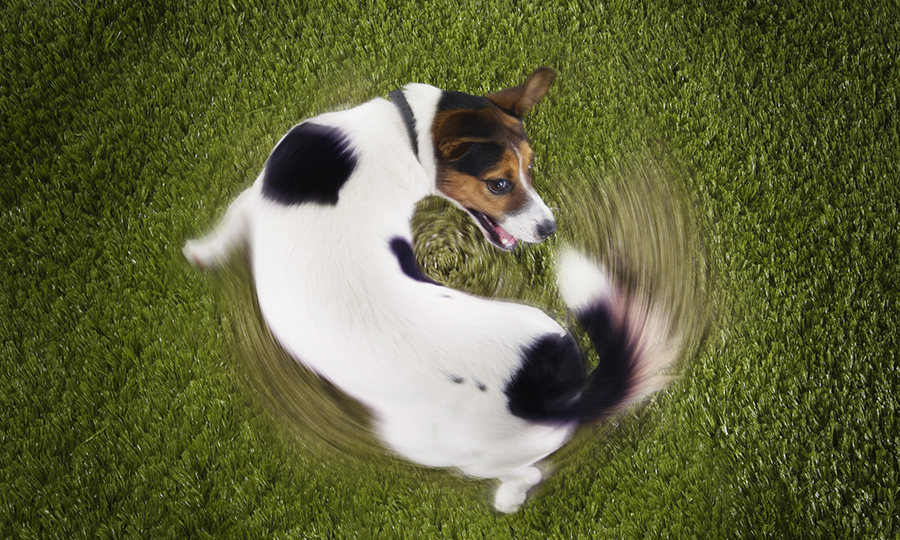


What is circling in dogs?
Although circling is a common behavior in puppies, it can occasionally indicate a more serious issue. A typical representation of normal circling behavior can appear when a puppy is simply entertaining themself by chasing their tail or circling before defecating. However, if circling becomes a frequent occurrence or an abnormal gait accompanies this symptom. It could be a sign of nerve damage, cognitive impairment, or ear problems. If you observe your pet walking strangely or this symptom persists for a long period, it is recommended to visit the vet to determine the exact cause of this behavior.
Common causes of circling in dogs
Temporary circling behavior can be considered normal in dogs, but if it persists, you may suspect one of the following health concerns.
-
Anxiety
A common trigger for circling behavior in dogs is anxiety-inducing situations and environments such as fireworks, thunder, a small living environment, or from a past traumatic event. There are genetic predispositions to anxiety in certain breeds and compulsive disorders that can cause circling behavior as well.
-
Liver disease
If your dog is suffering from liver disease, their body’s detoxification function will be compromised. This can cause an accumulation of toxins in their bloodstream which can give rise to various neurological symptoms such as circling.
-
Dog dementia or cognitive dysfunction syndrome (CDS)
This disease is similar to human dementia and Alzheimer's, with cognitive function deterioration caused by damage to nerve cells and the accumulation of beta-amyloid components in the brain. Although the exact cause is unknown, it is known to cause symptoms such as circling and frequent barking.
-
Brain tumor
Tumors in the brain can exert pressure that leads to neurological changes which can manifest as symptoms such as circling.
-
Brain damage
Trauma to the brain can lead to neurological symptoms such as circling.
-
When a dog has Cushing's disease, their hormones become imbalanced, which can lead to disruptions in their energy usage after meals. These disruptions can cause behavioral problems and, in some cases, may even result in circling behavior.
-
Ear infections and inflammation
When bacteria, fungi, or parasites cause ear infections, it can lead to a vestibular disorder that affects balance. Signs of an ear infection will show symptoms of circling and head tilting.
-
Idiopathic vestibular disease
The term "idiopathic" refers to a medical condition in which the exact cause is not known. In older dogs, vestibular diseases can manifest suddenly without any apparent reason, and among common symptoms is circling behavior.
Symptoms that accompany circling behavior in dogs
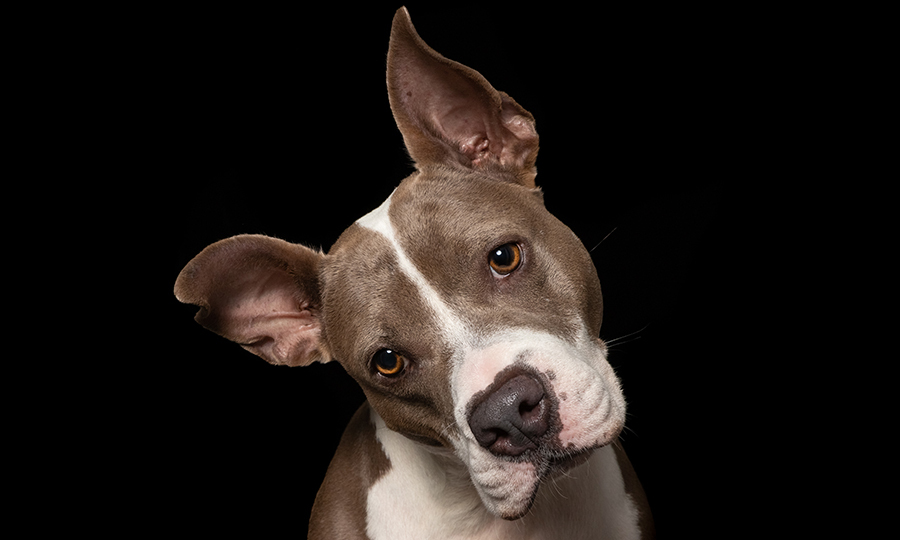

If a dog turns circles once or you can easily distract them from this behavior, it may not be a cause for concern. However, if this behavior occurs repeatedly and intensifies, it could indicate potential health problems for the dog.
Symptoms that may appear with circling behavior:
- Wandering around aimlessly
- Changes in sleep patterns or behavior
- Abnormal gait (their walking behavior becomes strange)
- Sudden changes in appetite (increase or increase)
- Air snapping or barking in the air
- Disorientation
- Seizures
- Ear odor, redness, or frequent head shaking
- Walking with head down or excessive drooling
- Head tilt to one side or uncontrollable eye movements
Risk in circling behavior in dogs and when to see a vet
Circling in dogs is typically linked to neurological symptoms, and it is generally attributed to brain damage, tumors, vestibular disease, or other related conditions. If you notice that you are unable to divert your dog’s attention easily with play or toys when they are circling or you notice an abnormal gait, you should check with your veterinarian as soon as possible. These signs of circling suggest a significant concern and should be met with medical attention before symptom progresses into something more severe such as seizures. Other symptoms such as head shaking, an inner ear infection, head tilting to one side, or rapid eye movements should also prompt a visit to the vet.
Home treatments for circling behavior in dogs
If your pet only shows this behavior once or once in a while, it can be considered normal doggy behavior. It is when the problem becomes frequent and other symptoms accompany the circling behavior that requires attention. Unfortunately, circling is associated with neurological causes that require a medical examination for accurate diagnosis and treatment. Since circling and other neurological symptoms can often lead to accidents, it's a good idea to keep pointed or hard objects away to avoid injury. In case seizure symptoms appear, applying pressure on the eyeball can activate the parasympathetic nerve that runs behind the eye, which can help stabilize them. There is only so much that can be done at home for these types of symptoms, so it is recommended to take them to a veterinary hospital as soon as you see symptoms worsening.
Diagnosing circling behavior in dogs
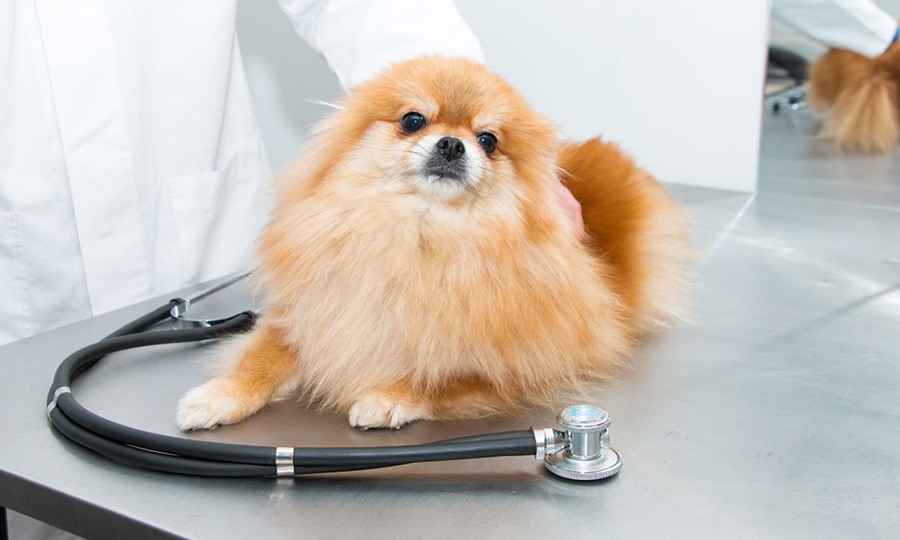

If you take your dog to the animal hospital for circling symptoms, it is best to come prepared with some of the following information for a quicker diagnosis and examination.
- How long have the symptoms lasted?
- When did you first begin to notice circling?
- Have you noticed any changes or abnormalities in the way your dog walks?
- Were there any recent bumps or trauma?
- Are there any other unusual symptoms that you have noticed?
Then the following tests may be performed to help determine the exact cause:
-
Blood tests
Blood tests are done to evaluate liver function and the presence of toxins.
-
Abdominal ultrasounds
Abdominal ultrasounds can check the overall shape of the liver and the presence of fibrosis.
-
CT scan
A CT scan is done to check for possible causes of symptoms in the liver or ears.
-
MRI scan
If circling is accompanied by neurological symptoms such as seizures, an MRI scan can be used to determine if there is a problem with the brain.
-
ACTH stimulation test
An ACTH stimulation test is a test to diagnose Cushing’s disease, which can cause symptoms of circling. This test takes a blood sample and measures the level of cortisol in the blood.
-
Neurological examination
It is a non-invasive test performed manually by a veterinarian to check cranial nerves, postural response, and spinal nerves.
Treatment for circling behavior in dogs
The treatment will depend on the underlying cause of the circling behavior.
-
Antibiotics
If it is caused by an ear infection, antibiotics and antifungal drugs are prescribed to treat the infection.
-
Hepatoprotective drugs
If symptoms appear due to abnormal liver function, hepatoprotection is prescribed. Surgery may be required if a portosystemic shunt (PSS) occurs, in which blood flow to the liver is abnormal.
-
Cancer treatment
If symptoms are caused by a brain tumor, it is treated through chemotherapy.
-
CDS management
Cognitive dysfunction syndrome cannot be cured, but it can be managed to an extent with medication.
-
Symptomatic treatment
If other neurological symptoms accompany circling, treatment is carried out accordingly. For example, if seizures occur, anti-seizure drugs may be prescribed to help control them.
Prognosis for treatment of circling in dogs
The prognosis for circling in dogs is contingent upon the underlying trigger. In certain instances, positive results may be prompt post-treatment; however, other causes will require long-term treatment.
Prevention of circling behavior in dogs
Preventing circling in dogs can be challenging. However, if your pet is an older dog, it is recommended that you carefully observe any changes in their behavior and energy levels. If you notice any of the symptoms above, the best form of prevention is preventing this behavior from worsening. It is recommended to visit the hospital immediately to determine the underlying cause.
Find out more about your dog’s symptoms and diseases on the Buddydoc app!
The Buddydoc library is filled with everything you’d want to know about each symptom and disease your pet may experience. If you would like to find out more about the causes, signs, treatments, preventions, and more for your dog’s disease. Try out the Buddydoc app and search for your pet’s symptoms or diseases in the Buddydoc library.