ARTICLE
How to Read Your Dog’s Body Language - Understanding Canine Behavior
페이지 정보
본문
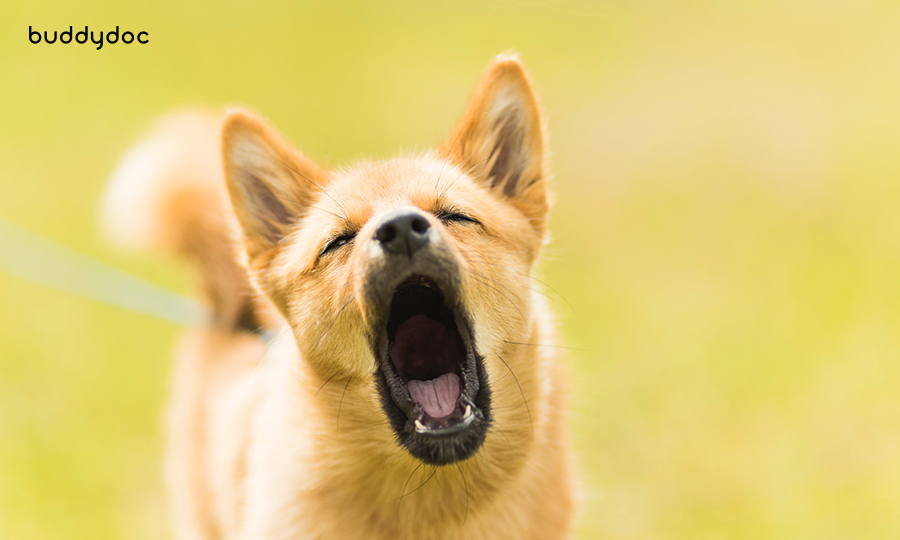


What is dog body language
Understanding your dog's body language is crucial for effective communication and building a stronger bond with your furry companion. Dogs communicate primarily through non-verbal cues, and deciphering their body language can provide valuable insights into their emotions, needs, and overall well-being. In this article, we will guide you through the fascinating world of dog body language, helping you interpret their signals and deepen your understanding of your canine companion.
Deciphering your dog’s body language
A dog’s non-verbal cues can be broken down into the following categories. We will go over each category and explain what type of insights you can gain from why they express these different body parts!
Facial expressions
Your dog's face holds important clues about their emotional state.
- Relaxed facial muscles and soft eyes indicate a calm and content dog. It signifies that they are comfortable and at ease.
- Dilated pupils, a furrowed brow, or a stiff gaze can indicate fear or anxiety. These signs suggest that your dog may be feeling threatened or uncomfortable in the situation.
- Bared teeth, a wrinkled nose, and a fixed stare may indicate aggression or discomfort. It's crucial to recognize these signs as potential warnings of aggression and to exercise caution.
Tail expressions
A dog's tail is a prominent communicator of their emotions. Consider the following tail positions and movements:
- A wagging tail with a loose, relaxed motion typically signifies happiness and friendliness. The more enthusiastic the wag, the more excited the dog is.
- A tucked tail or a stiffly held tail close to the body may indicate fear or submission. It suggests that your dog is feeling insecure or threatened in their environment.
- A high, stiffly wagging tail might signify alertness or possible aggression. Be cautious if you observe this tail position, as it could be a sign that your dog is on guard.
Posture and body movements
Your dog's body posture provides valuable insights into their confidence, mood, and intentions. Consider the following cues:
- A relaxed, loose body posture indicates a calm and content dog. They feel safe and comfortable in their surroundings.
- Crouching or slinking with a lowered body suggests fear or submission. Your dog may be feeling anxious or trying to convey their non-threatening nature.
- An erect, stiff posture with raised hairs on the back of the hind legs may signal aggression or alertness. It's essential to approach such dogs with caution and give them space.
Yawning and lip licking
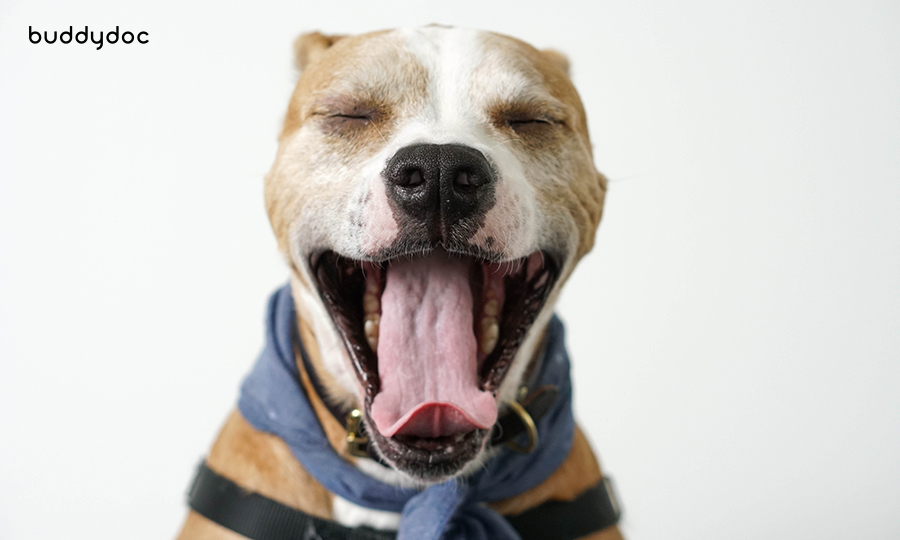

These behaviors often indicate stress, anxiety, or a need for appeasement. Here's what they can mean:
- Excessive yawning or lip licking may suggest discomfort or a desire to diffuse tension. Your dog might be trying to communicate that they are feeling uneasy or anxious.
Address the underlying cause of stress and provide a calm and safe environment for your dog. Offering reassurance and removing potential stressors can help alleviate their discomfort.
Paw lifting and stretching
Paw lifting and stretching have various meanings and intentions.
- Your dog may lift a paw as a sign of relaxation, preparing for play, or seeking attention. It's their way of engaging with you or expressing their readiness for a fun activity.
Respond positively to these behaviors by engaging in gentle play or offering attention and affection. It strengthens the bond between you and reinforces positive behaviors.
Rolling over
Rolling over can convey different messages, depending on the context. Understand the following possibilities:
- Your dog may roll over as a submissive gesture, an invitation for belly rubs, or during play. It's a vulnerable position that signifies trust and a desire for positive interaction.
Respect your dog's boundaries and comfort level when responding to this behavior. Provide gentle belly rubs if they enjoy it, but never force them into this position.
What your dog is trying to tell you
From barks and growls to whining and howling, your dog’s verbal cues can be deciphered in various ways depending on the context, time of day, etc. The following is a good idea of why your dog may be expressing themselves in this verbal way.
Barking
Barking is a form of communication with diverse meanings.
- The tone, pitch, and frequency of barks can indicate excitement, fear, alertness, or attention-seeking. It's important to differentiate between different types of barks.
- The different types of barking can be divided into six categories; alert barking, playful barking, demand barking, anxiety/fear barking, aggressive barking, and boredom/attention-seeking barking.
Determine the underlying cause of barking and respond accordingly to address your dog's needs. For example, if your dog barks out of fear, provide reassurance and remove the source of their distress.
Growling and snarling
Growling and snarling serve as warning signs or expressions of discomfort.
- Respect your dog's warning signals and provide space to alleviate their discomfort. Never punish or scold a dog for growling, as it may escalate the situation.
- Consult with a professional dog trainer or behaviorist if aggression issues persist. They can guide you in managing and modifying such behavior.
Whining and howling
Whining and howling can convey a range of emotions and needs.
- Your dog may whine or howl to express anxiety, seek attention, or communicate discomfort. It's important to investigate the potential cause behind these vocalizations.
Create a secure and calm environment for your dog, addressing any underlying anxiety or discomfort. Provide appropriate outlets for their needs and ensure they feel safe and supported.
Conclusion: Understanding your dog’s communication
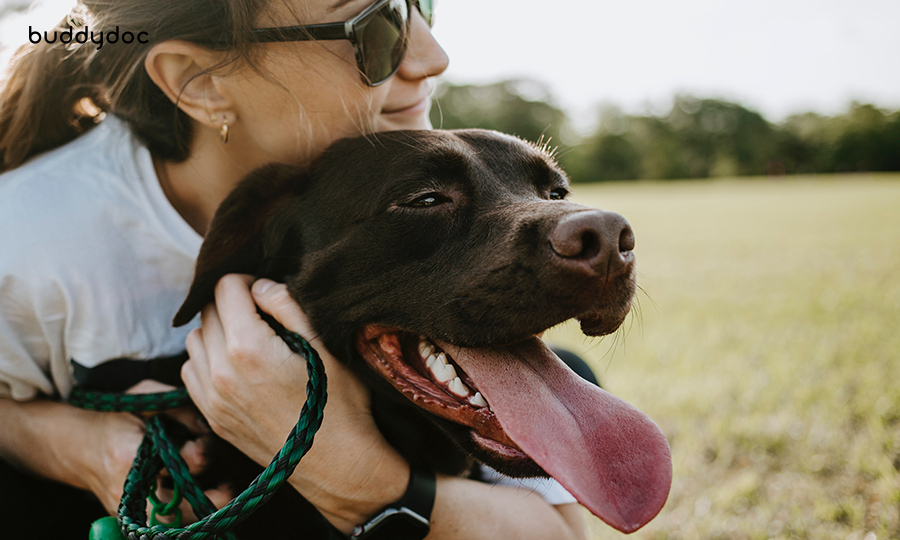

By understanding and interpreting your dog's verbal and nonverbal cues, you can develop a deeper connection and strengthen your bond with your puppy. Pay attention to facial expressions, tail language, posture, and other non-verbal cues. Remember that context is crucial in interpreting your dog's behavior accurately. Approach their body language with patience, empathy, and a willingness to learn. By making an effort to understand their body language, you can enhance communication, build trust, and provide the best possible care for your dog!
Read more on the Buddydoc blog page!
Buddydoc provides a weekly updated blog to keep you informed on the latest and best ways to prepare and take care of your pet all year round. Check out more articles you may be interested in!