SYMPTOMS
Stomach Swelling in Dogs (Abdominal Distension) - Causes and Treatment…
페이지 정보
본문


What is stomach swelling in dogs?
Stomach swelling, also known as abdominal distension, in dogs can have a variety of causes, some of which may be normal and some may be more serious. Bloating can be a sign of a serious emergency and can cause discomfort and pain for dogs. It's important to note that a bulging belly due to obesity or pregnancy may sometimes be mistaken for bloating. The causes of a swollen abdomen can range from relatively minor issues like obesity to serious conditions like uterine empyema and bloating.
The main causes of abdominal swelling in dogs
There are many causes of abdominal swelling in dogs. They range from relatively minor conditions to emergency situations that require a quick visit to the hospital.
Causes of abdominal bloating include:
-
Intestinal parasitic infections
Parasites in the intestines can cause bloating. It usually occurs more often in young puppies and results in a bulging belly.
-
Obesity
When dogs overeat and remain inactive, fat accumulates in the abdomen and causes the belly to protrude over time. Sometimes obesity may suggest a hormonal disorder is present in your dog.
-
Pregnancy
In female dogs, pregnancy can cause the belly to protrude.
-
Infection of the uterus
A condition that occurs in female dogs and can cause abdominal distension.
-
Peritonitis
The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that covers the abdominal organs, and when this area becomes inflamed, called peritonitis, can cause abdominal distension.
-
Organ enlargement
Organ enlargement is caused by pathological conditions such as infections, inflammatory reactions, and tumors which can cause the stomach to swell.
-
Accumulation of ascites (Abdominal effusion or build-up of fluids)
Ascites is when too much fluid builds up in the abdominal cavity for a variety of reasons. It can be caused by internal bleeding from shock or trauma, damage to the bladder that causes urine to build up, liver disease, heart disease, tumors, or inflammatory reactions.
-
Hypothyroidism
It occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones. Hypothyroidism slows down the body's metabolic function, which can lead to weight gain and fat accumulation, even when little food is eaten.
-
Hyperadrenocorticism (Cushing's disease)
Abdominal distension can occur due to abnormal function of the adrenal gland, causing the liver to enlarge, fat accumulating in the abdomen, and thinning the dog’s skin.

-
Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus (GDV)
Bloat is common in large breeds of deep-chested breeds prone to GDV, such as Great Danes, St. Bernards, and German Shepherds. Gas, food, and fluid fill the stomach and small intestine, causing bloating. It can also create an emergency in which the stomach is twisted.
Common symptoms that can occur with stomach swelling in dogs
In general, symptoms that may appear along with a dog's bloating include:
- Discomfort or pain when touching the abdomen
- Loss of appetite, lethargy, exercise intolerance
- Shortness of breath, gasping, drooling
- Vomiting and diarrhea
- Changes in urinary habits
Accompanying symptoms may vary depending on the cause of stomach swelling in dogs
- May be accompanied by diarrhea if the cause is an intestinal parasitic infection.
- If caused by hormonal diseases such as hypothyroidism or hyperadrenocorticism, symptoms such as polyuria, decreased energy, and hair loss may be accompanied.
- If your dog has ascites, you may feel a pulsating sensation when you touch their stomach.
- Bloat may be accompanied by symptoms such as severe abdominal pain, panting, rapid breathing, and excessive drooling.
When to see a vet for stomach swelling in your dog
Sudden bloating can be a sign of a serious illness, so it's best to see your doctor right away. Causes such as parasitic infections can be treated relatively simply with medication, but if they are caused by hormonal disorders or tumors, the condition may worsen over time. If your dog feels pain due to the stomach swelling or is accompanied by clinical symptoms such as diarrhea, loss of energy, or fever, you need to visit the hospital right away for examination and treatment.
In particular, if symptoms such as rapid breathing, excessive salivation, and inability to stand up with abdominal pain appear, it may indicate an emergency in which the stomach is twisted when left unattended.
How to manage stomach swelling in dogs at home
If the symptoms are not severe, you can try light exercise or taking extra walks and eating foods like cooked plain pumpkin or probiotics to help with digestion. If the problem is caused by gas, you can try taking over-the-counter medications that have gas-removing properties, like Gas-X (simethicone). If the issue is simply due to obesity, it's recommended to increase your physical activity with snack intake adjustments and take frequent walks.
How is stomach swelling diagnosed in dogs at the hospital
When you visit the animal hospital, a veterinarian will ask you a series of questions to try to determine the cause of the bloating in your dog. They will also perform a physical examination, including palpation and inspection. Based on the results of the physical examination and your answers to the questions, the veterinarian will conduct additional tests.
Here are some questions a veterinarian may ask for a dog with a swollen stomach.
- When did the bloating start?
- How quickly did the bloating develop?
- Does your dog drink a lot of water or urinate often?
- How is the dog's vitality?
During the physical examination, a veterinarian will palpate all parts of the dog to check for any abnormalities, auscultate, and lightly percuss the abdomen to help determine the cause of the bloating.
For a more accurate diagnosis, the following tests can be performed:
-
Complete blood count (CBC)
A blood test involves drawing blood and running it through a machine to gather information about the blood cells, such as white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. If anemia due to intra-abdominal bleeding is present, the test results may show a decrease in the number of red blood cells. On the other hand, if inflammation is present, an increase in inflammatory cells can be detected through the test results.
-
Plasma biochemistry test - Serum biochemistry
To test for certain conditions, blood is collected and centrifuged to extract only the plasma. This can help determine which organ might be experiencing problems. For example, elevated liver levels may indicate Cushing's disease, while high cholesterol levels may suggest hypothyroidism. Biochemical tests can help distinguish the primary disease that can cause stomach swelling in dogs.
-
Urine test
Urine specific gravity, a urine stick, or microscopic observation can be used to confirm that the results of the urine test and the blood test are consistent.
-
Hormonal disease tests
If abdominal distension is suspected to be caused by hormonal disorders, specific testing for various disorders can be conducted.
-
Imaging tests
Imaging techniques such as radiography, abdominal ultrasound, and CT scan can be used to examine the organs in the abdominal cavity.
-
Biopsy
If abdominal distension is caused by ascites, multiple evaluations may be performed. A microscope can be used to examine the cells present in the ascites. If the bloating is caused by a tumor, a biopsy may be conducted to determine the type of tumor and to plan treatment.
-
Bacterial culture test
Bacterial culture test helps to confirm if a bacterial infection is present.
How is stomach swelling in dogs treated in a hospital?
Treatment for stomach swelling in dogs will depend on the cause. If the abdominal distension is due to obesity, it can be managed through diet and exercise. However, if it is caused by a medical condition, treatment from a veterinarian will be prescribed.
The following treatments are available for the various causes of stomach swelling in dogs:
-
Abdominocentesis
If ascites is present, the cause can often be inferred by removing the ascites through a syringe and analyzing its components. If the underlying cause of the ascites is not addressed, the ascites may continue to occur.
-
Hormonal disorders treatment
Abdominal distension that is caused by hormonal disorders requires treatment that is specific to the disorder. For example, if hypothyroidism is causing abdominal distension, a veterinarian may prescribe the drug Levothyroxine. On the other hand, if hyperadrenocorticism is the cause of the distension, a drug called Trilostane may be prescribed. In either case, the treatment is tailored to the specific disease causing the abdominal distension.
-
Chemotherapy & surgical removal
Abdominal distension caused by a tumor is treated with chemotherapy or surgical removal.
-
Surgical correction
Bloating can be a very dangerous condition that can cause gastric torsion. If bloat is caused solely by gas without gastric torsion, it can be stabilized by removing gas from the intestine with medication without requiring surgical correction. However, if gastric torsion has occurred, surgery must be performed promptly. If left untreated for a long time, poor blood flow to the stomach may cause significant damage. In this case, a surgery called gastropexy is performed. The prognosis may be poor in cases where clinical symptoms last for more than 6 hours, arrhythmia can occur, part of the stomach may need to be removed, or the spleen may need to be removed.
-
Peritonitis
Peritonitis can be diagnosed using an abdominal ultrasound. It is typically caused by problems with organs in the abdominal cavity or due to trauma. Treatment of the underlying cause of peritonitis will usually resolve the condition, but if it is severe, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed.
How to prevent stomach swelling in dogs
Preventing the disease may be difficult, but diet and exercise are often necessary to prevent swelling in the stomach. Periodically tracking and monitoring your dog's weight can also help detect health abnormalities and sudden bloating. If your dog tends to eat quickly, it's a good idea to feed them in small amounts more frequently instead. It's best to avoid letting your dog drink large amounts of water at once and to avoid strenuous exercise immediately after eating.
Check stomach swelling and bloating symptoms with the Buddydoc Symptom Checker!
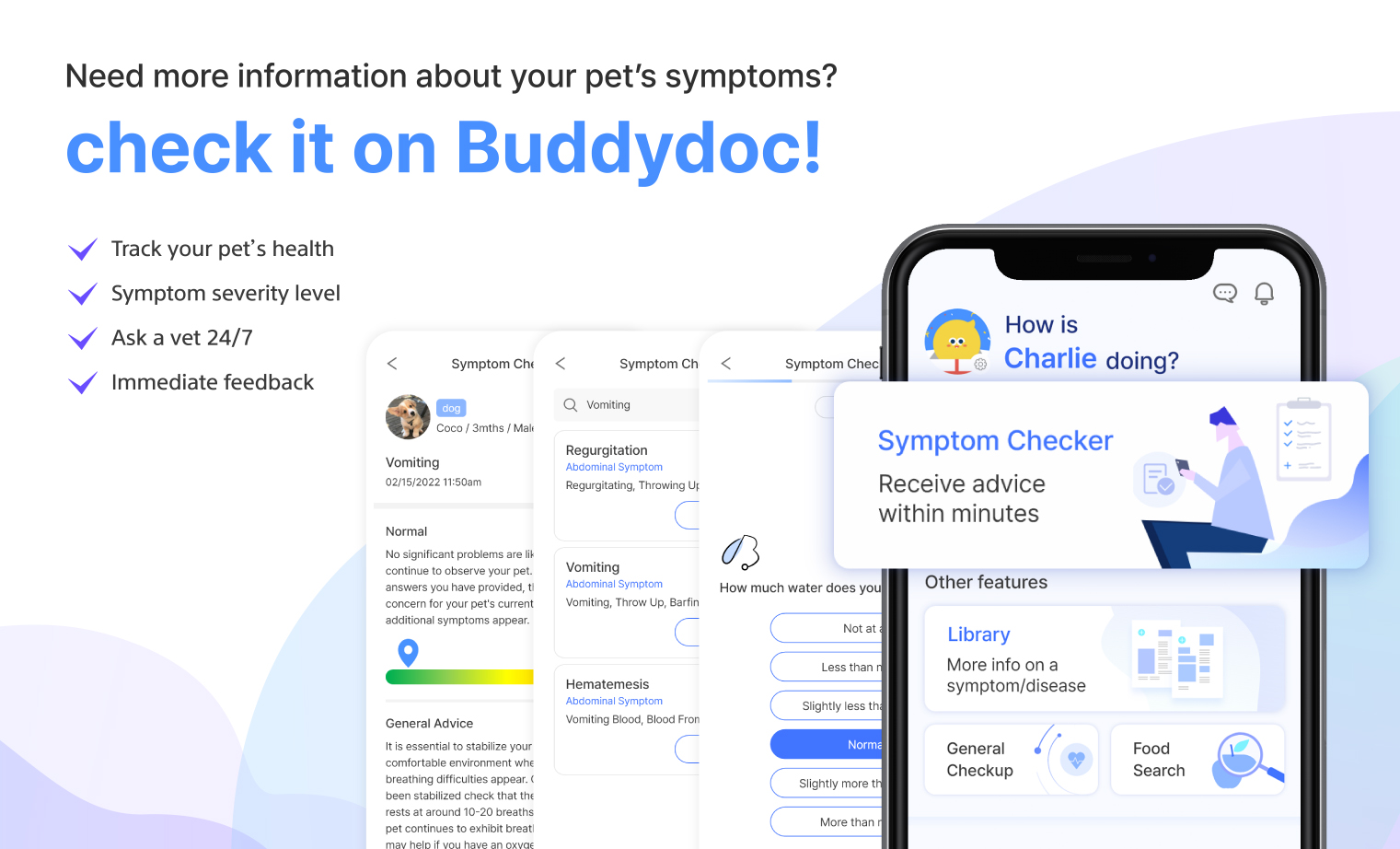
If it is difficult to accurately determine the severity of the symptom, you can use the Buddydoc symptom checker to help you! The self-symptom checker service will ask questions about your pet’s symptoms and can take anywhere from 2-5 minutes to receive a pet triage result. Each answer you provide has a triage value and is calculated in the end result page to help you make a better decision for your pet’s health. The result page provides a level of risk to your pet’s health, veterinarian advice, possible diagnoses, and recommended examinations when visiting the hospital.